ISO27001, SOC2, PDPA, and GDPR These acronyms refer to various standards, regulations, and guidelines related to information security, privacy, and web application security.
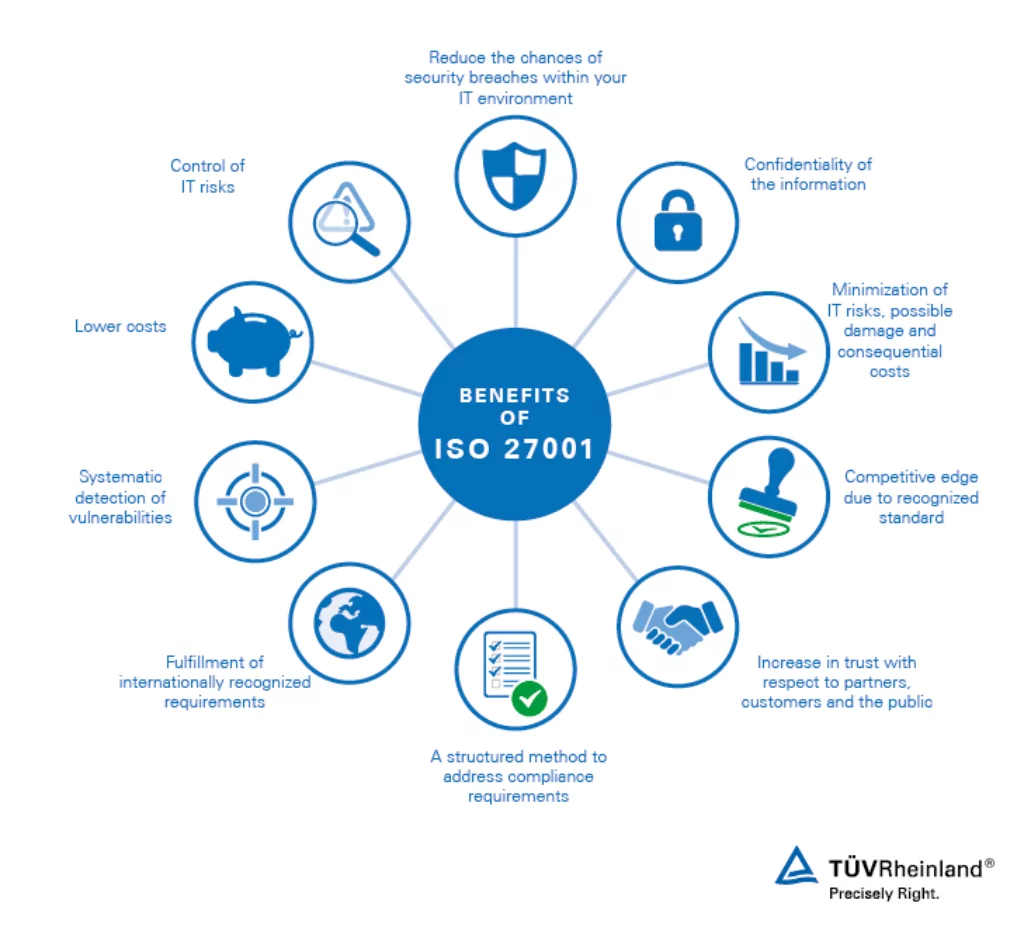
- ISO27001: ISO/IEC 27001 is an internationally recognized information security management system (ISMS) standard. It systematically manages sensitive information by applying risk management processes, ensuring the data remains secure. Organizations can get certified to demonstrate their commitment to information security and compliance with the standard.
- SOC2: Service Organization Control 2 (SOC 2) is a criterion for managing customer data based on five “trust service principles”: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. It is an audit framework designed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) to help service providers assure their clients that their information systems meet the necessary requirements in these areas.
- PDPA: The Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) is a collection of laws or regulations governing personal data protection in various jurisdictions. For example, Singapore’s Personal Data Protection Act establishes a data protection law to govern private data collection, use, disclosure, and care. The specifics of PDPA may vary between countries, but the general goal is to protect individuals’ privacy and personal information.
- GDPR: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data protection and privacy regulation that applies to organizations operating within the European Union (EU) and European Economic Area (EEA). It also affects organizations outside these regions if they process the personal data of individuals within the EU/EEA. GDPR aims to give individuals more control over their personal data and ensure that organizations responsibly, securely, and transparently handle it. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines.
Fintech organizations, like any other organizations handling sensitive data, can implement the ISO27001, SOC2, PDPA, and GDPR standards and guidelines by following a series of steps that help ensure compliance and enhance their overall security posture. Here’s how they can approach each standard:
- ISO27001:
- Perform a risk assessment to identify information assets, threats, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts.
- Establish an Information Security Management System (ISMS) based on the ISO27001 framework, including information security policies and procedures.
- Implement security controls per ISO27001’s Annex A, which outlines 114 rules across 14 domains tailored to the organization’s risk profile.
- Train employees to understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining information security.
- Conduct regular internal audits and management reviews of the ISMS to ensure ongoing effectiveness and compliance.
- Obtain certification from an accredited certification body to validate the organization’s adherence to the ISO27001 standard.
- SOC2:
- Identify the applicable trust service principles (security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy) based on the organization’s specific services and client requirements.
- Develop and document policies, procedures, and controls addressing each relevant trust service principle.
- Train employees on the organization’s SOC2-related policies and procedures.
- Conduct a gap analysis to identify areas where the organization’s controls may not meet SOC2 requirements.
- Address identified gaps and implement any necessary improvements.
- Engage an independent auditor to perform a SOC2 audit and provide a SOC2 report, which can be shared with clients to demonstrate compliance.
- PDPA:
- Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to ensure compliance with the applicable PDPA.
- Identify the types of personal data collected, processed, and stored by the organization.
- Develop and implement data protection policies, procedures, and practices that comply with the PDPA’s requirements (e.g., consent, data access, and correction, data retention, etc.).
- Implement security measures to protect personal data against unauthorized access, disclosure, and other risks.
- Train employees on data protection principles and their responsibilities under the PDPA.
- Establish processes for handling data breaches, including notification and reporting requirements.
- GDPR:
- Identify whether the organization is subject to GDPR and whether it acts as a data controller or data processor.
- Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) if required by the GDPR.
- Perform a data mapping exercise to understand the flow of personal data within the organization.
- Implement GDPR-compliant policies and procedures, including obtaining consent, handling data subject requests, data breach reporting, and data retention.
- Incorporate privacy by design and privacy by default principles in the organization’s product and service development.
- Conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) for high-risk processing activities.
- Establish data processing agreements with third-party data processors to ensure GDPR compliance throughout the data processing chain.
Various tools and solutions are available to help organizations implement the ISO27001, SOC2, PDPA, GDPR, and standards and guidelines. Some tools may be specific to a particular standard, while others can be used across multiple standards. Here’s a list of some tools and solutions that can help:
- ISO27001:
- Risk assessment tools: Tools like vsRisk, Eramba, and RiskWatch can help organizations conduct risk assessments, identify vulnerabilities, and manage risks.
- ISMS tools: Solutions like ISMS.online, StandardFusion, and MyEasyISO can help in the development, implementation, and management of an Information Security Management System.
- SOC2:
- Compliance management tools: Platforms such as ZenGRC, StandardFusion, and Hyperproof can help organizations manage their compliance efforts, track controls, and streamline the audit process.
- Continuous monitoring tools: Solutions like Datadog, Splunk, and Sumo Logic can help organizations monitor their infrastructure, detect anomalies, and meet SOC2’s continuous monitoring requirements.
- PDPA and GDPR:
- Data mapping and inventory tools: OneTrust, TrustArc, and BigID can help organizations discover, classify, and manage personal data, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
- Privacy management platforms: Comprehensive privacy management solutions like OneTrust and TrustArc provide a range of tools for GDPR and PDPA compliance, including consent management, data subject request management, and data breach notification.
- Data protection impact assessment (DPIA) tools: Solutions like OneTrust and TrustArc also offer built-in DPIA templates and workflows to help organizations conduct DPIAs as required by the GDPR.